Solubility of Gases in Liquids
Solubility of Gases in Liquids: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Solubility, Solubility of a Gas in a Liquid, Solubility of a Solid in a Liquid, Effect of Temperature on Solubility of a Solid in a Liquid and, General Rule for Solubility
Important Questions on Solubility of Gases in Liquids
The molar solubility (in ) of a sparingly soluble salt is ‘s’. The corresponding solubility product is ‘s’ is given in terms of by the relation :
The percentage of oxygen in air is about . But the oxygen cylinder meant to be carried by deep sea divers contains about oxygen. Why is there a difference in the percentage of oxygen?
Dissolution of a solid X in water is exothermic. How does its solubility change with temperature?
Assume that the solubilities of and are the same at a given temperature. A saturated solution of is taken at that temperature and solid is added to it. The amount of added is such that all the ions present in the solution get precipitated as . What will be the state of the solution in terms of saturation?
Two saturated aqueous solutions A and B using the same solute are prepared at and , respectively. The densities of A and B are and at the given temperatures of solution A is heated to from . of solute is added to it in order to saturate it. Then this solution is cooled to and solute is precipitated. Consider the density of water as at all the given temperatures and the addition of solute in water does not alter the volume of the solution. Calculate the density of the solution in at .
Two saturated aqueous solutions A and B using the same solute are prepared at and , respectively. The densities of A and B are and at the given temperatures of solution A is heated to from . of solute is added to it in order to saturate it. Then this solution is cooled to and solute is precipitated. Consider the density of water as at all the given temperatures and the addition of solute in water does not alter the volume of the solution. Calculate .
Two saturated aqueous solutions A and B using the same solute are prepared at and , respectively. The densities of A and B are and at the given temperatures of solution A is heated to from . of solute is added to it in order to saturate it. Then this solution is cooled to and solute is precipitated. Consider the density of water as at all the given temperatures and the addition of solute in water does not alter the volume of the solution.
Calculate the solubility of the solute at and .
The solubility of a salt is at . If its relative molecular mass is , calculate the number of molecules of solute present in of saturated solution.
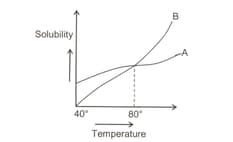
Observe the given curves. Saturated solutions of A and B are cooled from to . Which of the above curves is associated with the formation of more amount of precipitate?
The solubility of a solute is at and to . If of solvent is made to saturate with the solute at , what is the amount of precipitate formed at ?
Calculate the solubility of the solute, if of solute is present in of saturated solution at a given temperature.
Solubility of a salt in water is at . Calculate the amount of the salt required to saturate water at .
Select the appropriate option for the following statements:
Statement : In concentrated solution, the molecular mass of the solute is unusual.
Statement : In concentrated solutions intermolecular attraction between molecules is strong.
Suman took two glasses of water from a water filter. She cools one glass in a fridge and warms the other glass on a stove.
Which glass of water will hold more dissolved oxygen?
Explain using Henry's law?
In which solution solubility ofis less than that in pure water?
Non polar compounds soluble in polar solvent.
How many grams of carbon dioxide gas is dissolved in a bottle of carbonated water if the manufacturer uses a pressure of in the bottling process at ?
Given: of in water at .
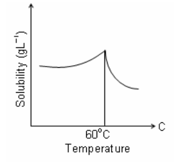
Solubility curve of a hydrated salt in water with temperature is given. The curve indicates that the solution process is
Solubility of a gas in al liquid increases with
Henry's law is valid for
A) Ammonia gas dissolution in water
B) gas dissolution in unsaturated blood
C) dissolution in water
D) dissolution in water
